These copies of the Industrial Cooperative Association (ICA) Model By-Laws go from an early version from the late 1970s to the mature version in the early 1980s. Also included are a report from the late 1980s on how to set up a democratic worker ownership trusts written for Zimbabwe plus a law journal article on the 1982 Massachusetts law on Employee Cooperative Corporations.
Marginal Productivity Theory versus Labor Theory of Property
This paper shows that MP theory can also be formulated in a mathematically equivalent way using vectorial marginal products–which however conflicts with the “distributive shares” picture.
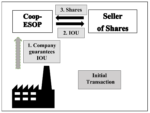
On Employee Ownership Trusts (EOTs)
This paper explores the Employee Ownership Trust (EOT) model, comparing it with traditional partnerships and employee ownership structures like the US ESOPs and the European Coop-ESOPs.
Market Valuations are Inappropriate for Employee-Owned Firms
Any `fair market valuation’ of an employee-owned firm or partnership that assumes those future residuals accrue to the current shareholder/residual-claimants is inappropriate.
Classical Liberalism and the Abolition of Certain Voluntary Contracts
This paper analyzes three contracts and shows that there is indeed a deeper democratic or Enlightenment classical liberal tradition of jurisprudence that rules out those contracts. The ‘problem’ is that the same principles imply the abolition of the employment contract, the contract for renting human beings, which is the foundation for the economic system that is often (but superficially) identified with classical liberalism itself. Frank Knight is taken throughout as the exemplary advocate of the economics of conventional classical liberalism.
Fallacies about corporations
This article comments on Isabelle Ferreras’s “Democratizing the Corporation.” The focus is on the conceptual framing, which arguably contains a number of problems that are quite common on the left and are thus doubly deserving of commentary and explanation.
Is “Capitalism” a Misnomer? On Marx’s “capitalism” and Knight’s “civilization”
This is an open access article from the European Journal of the History of Economic Thought.
The name “capitalism” derives from Marx’s false analogy between medieval land ownership and the “ownership of the means of production.” However, unlike medieval land, capital goods can be rented out, e.g., by Frank Knight’s entrepreneur, and then the capital owner does not hold those management or product rights. What then is the characteristic institution in our civilization? It is the voluntary renting of workers. What then is the relationship between Classical Liberalism, the dominant philosophy behind Economics, and a lifetime labor contract? Frank Knight had plenty to say against the doctrine of inalienable rights which disallows such contracts.
The Kantian Person/Thing Principle in Political Economy
This is Chapter 4 in my book: Ellerman, David. 1995. Intellectual Trespassing as a Way of Life: Essays in Philosophy, Economics, and Mathematics. Lanham MD: Rowman & Littlefield.
Ethical theories can be broadly grouped into utilitarian theories and rights-based theories. Modern economics is so thoroughly utilitarian that most economists would be hard-pressed to cite the application of a rights-based argument to economic institutions. Yet the normative principles outlined in the first two chapters, the labor theory of property and the de facto theory of inalienability, are squarely within the rights-based tradition. The democratic principle of self-determination is also a closely allied rights-based theory [see Ellerman 1992].
Myth and Metaphor in Orthodox Economics
This is Chapter 2 from: Ellerman, David. 1995. Intellectual Trespassing as a Way of Life: Essays in Philosophy, Economics, and Mathematics. Lanham MD: Rowman & Littlefield.
Discussion of the fundamental questions of political economy is today almost completely clouded and distorted by a number of basic myths and metaphors. Deconstruction is necessary before constructive discussions can begin. The myths and metaphors are concerned with basic conceptions about property and contract, not with prices and markets. As layer upon layer of distortions are removed, new facts and new perspectives on old facts will emerge. These facts have fairly direct normative implications, but the disagreements and controversies are about the facts, not about norms or prescriptions.