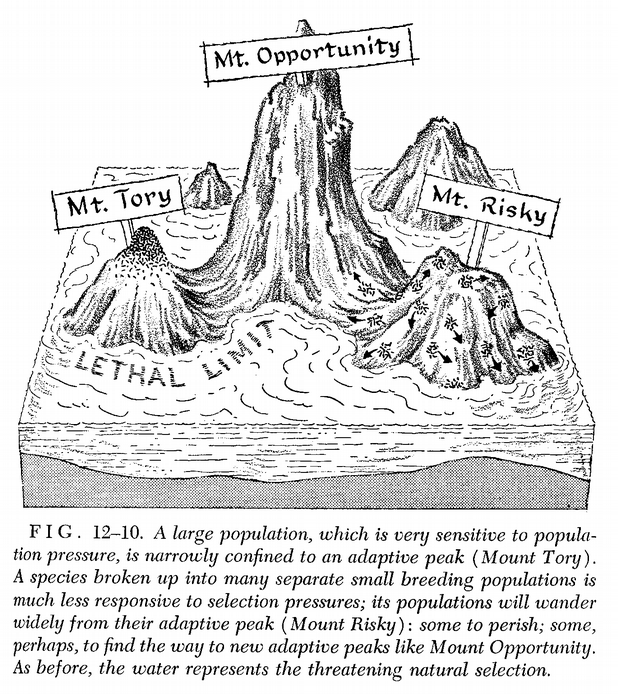
Evolutionary economics often focuses on the comparison between economic competition and the process of natural selection to select the fitter members of a given population. But that neglects the other “half” of an evolutionary process, the mechanism for the generation of new possibilities that is key to dynamic efficiency. My topic is the process of parallel experimentation which I take to be a process of multiple experiments running concurrently with some form of common goal, with some semi-isolation between the experiments, with benchmarking comparisons made between the experiments, and with the “migration” of discoveries between experiments wherever possible to ratchet up the performance of the group. The thesis is that parallel experimentation is a fundamental dynamic efficiency scheme to enhance and accelerate variation, innovation, and learning in contexts of genuine uncertainty or known ignorance. Within evolutionary biology, this type of parallel experimentation scheme was developed in Sewall Wright’s shifting balance theory of evolution. It addressed the rather neglected topic of how a population on a low fitness peak might eventually be able to go “downhill” against selective pressures, traverse a valley of low fitness, and then ascend a higher fitness peak. The theme of parallel experimentation is used to recast and pull together dynamic and pluralistic theories in economics, political theory, philosophy of science, and social learning.
This is a reprint from the Journal of Bioeconomics.