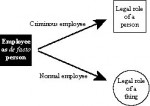
To answer the “best case” voluntary-contractarian arguments for slavery and autocracy, the democratic and antislavery movements forged arguments not simply in favor of consent but arguments that voluntary contracts to legally alienate aspects of personhood were invalid “even with consent”—which made the underlying rights inherently inalienable. Once understood, those arguments have the perhaps “unintended consequence” of ruling out today’s self-rental contract, the employer-employee contract.
On the Renting of Persons: The Neo-Abolitionist Case Against Today’s Peculiar Institution
March 24, 2015 by
Inalienable Rights: Part I The Basic Argument
March 4, 2010 by
What is the inalienable rights theory that descends from the Reformation through the Enlightenment and that answers the classical apologies for slavery and autocracy based on implicit or explicit voluntary contracts?